

From the fingertips of today’s youth to the intricate interplay of online networks they weave, the pervasive influence of the digital era engulfs our youngest consumers. As social media proliferates, we are relentlessly bombarded with advertisements. A burgeoning market emerges through the waves of ever-growing social media platforms alongside a fierce young market raised against the bright lights of the digital epoch -the “influencer economy”.
Inundated by covert advertising, social media platforms serve as a hotbed for businesses to market and sell products. The influencer economy emerges from the sheer accessibility and ubiquity of information coupled with an enhanced focus on user-generated content. Because the ‘influencer’ is no superstar, nor celebrity- but rather the common individual. It is through the means of social media platforms through which influencers gain their popularity. As new-media arbiters, influencers amass large followings, ranging from tens of thousands to millions. In doing so, they rake in exorbitant amounts of money in exchange for brand deals and endorsements marketed towards their followers. Their supposedly humble roots leverage the shaping of brand reputation and loyalty, with 69% of consumers valuing influencers as their purchase informers of choice. Followers look up to influencers as faces of authenticity, forming strong para-social bonds as the line between social media star and trusted friend are blurred.
A large subset of consumers affected by influencer marketing are today’s youth, particularly Gen Alpha and Gen Z. In fact, both of these generations constitute the most extensive demographic of social media users, using such platforms in a volume incomparable to prior generations. The great technological shift in the 2010’s surmounted to these digital natives being almost raised by the internet, since they have been continuously barraged with marketing ploys and online advertisements since childhood. This highlights a pronounced shift in ideology, especially regarding the consumption and interpretation of information.

Source: Flickr
Social Media’s Economic and Psychological Impacts on Youth
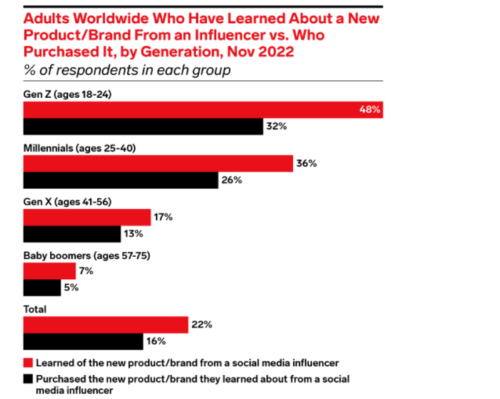
The effects of social media on the development and socialization of children has become a contentious topic. Children usually capture images vulnerability and innocence sheltered from adulthood’s turmoils. However, now with the sudden influx of influencer marketing schemes, it is children and teenagers who have been identified as a key target market – young enough to foster brand loyalty and keen enough to sway adult decision makers. In recent discussion, issues regarding worsened mental health are cited as results of high social media usage. This is further corroborated by a 2023 study that delineated reducing screen-time resulted in an increase in self-esteem and body image confidence. Now with younger generations becoming increasingly expressive and exposed to the internet and social media, some concerns have been raised. This is particularly apparent on social media platforms such as Tiktok and Instagram hosting both a large volume of influencers and a formidable amount of younger Gen Z and older Gen Alpha users.
Source: InsiderIntelligence
For example, targeting adult skincare like retinol and moisturizers to gullible children emphasizes the significant impact influencers wield over young audiences and the potential psychological issues that may result. As these issues propagate, it further adds to skewing of market dynamics and raises issues about the imperfect information dissemination on these diverse platforms, especially to more vulnerable demographics. Imperfect information, as economics suggest, leads to market failure and a sharp hedging toward unwise spending.
Due to the enabling of imperfect information and carefully sketched facades of authenticity, nano, micro to macro influencers have established a lucrative ecosystem where everyone can make something for their pockets. The higher they rise, the higher the fee they charge for their collaboration. According to Shopify data, payment per brand partnership ranges from $10-1000 for nano influencers with 1,000 – 10,000 followers all the way to $10,000 per post for mega influencers with more than 1,000,000 followers. Meanwhile, the average cost for a sponsored Tiktok or YouTube video are estimated to be $3,514 and $4,491 respectively. At the same time, influencers indulge themselves in free brand gifts, whether it is a product, a service or even a free VIP ticket.
One then wonders at the source of the endless dollar flow. The answer to this question lies in the nature of their target audience. Born between 1997 and 2012, GenZ are the first-ever generation to have grown up in a world dominated by smartphones and is also the largest generation in history by sheer magnitude. Hence, these young people have become the power engine of the global social media economy. According to Bloomberg, generation Z has as much as $360 billion at their disposal, a number that is more than double of its estimate a year ago.
To better capture their attention and satisfy their demands, social media apps such as Tiktok and Instagram have gained an increasing dominance in the world of marketing, with the number of influencer partnerships skyrocketing over the past few years. In 2022, the industry was valued at $16.4 billion and forecasted to reach $143.10 billion by 2030. However, the low barrier of entry to the world of influencers, and largely unregulated nature of social media marketing, where platforms are mere conduits for user-generated content has resulted in significant issues. Content creators do not need to be qualified or comply with certain ethical or moral standards, while the type and target of advertisement remains largely unsupervised. Inevitably, this environment free of regulation has become the ideal platform for any type of advertising to take root, even the more subtly alarming type that targets demographics as young as children.

Source: LinkedIn
Risk Mitigation: The Value of Regulatory Intervention in Social Media
In recent years the world has witnessed the ascension of influencer marketing into a multi-billion dollar industry, with social media personalities highly instrumental to the purchasing decisions of their followers. However, with this rise in prominence, concerns proliferate about transparency, authenticity, and ethical practices. To address these challenges, various regulatory measures have been implemented. This is a crucial mitigation strategy, for industry, consumers and advertisers alike.
One key aspect of regulation in social media marketing is the requirement for influencers to disclose their sponsored content. Federal agencies around the world such as the US Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) have provided guidelines that mandate influencers to clearly and conspicuously disclose their relationships with brands. This disclosure is commonly done using hashtags like #ad or #sponsored. Such declarations are essential for reinforcing transparency and helping consumers make more informed choices. Failure to comply with these guidelines can result in fines or other penalties.
Beyond federal regulations, social media platforms have implemented their own rules and policies. Platforms like Instagram and YouTube have introduced tools for influencers to label their posts as sponsored or paid partnerships. Not only does this support compliance with FTC guidelines but it is also instrumental in platforms promoting a positive user experience.
Furthermore, influencers are beginning to take self-regulation seriously. Many industry associations and groups have formed to establish ethical standards and best practices. These self-regulatory efforts ensure that influencers comply with integrity guidelines voluntarily.
The regulation of influencers around the world is a multifaceted endeavor that involves federal oversight, platform-specific rules, and influencer-driven self-regulation. These measures collectively work to promote transparency, authenticity, and ethical practices within the industry. While challenges persist, the evolving landscape of influencer regulation reflects a commitment to consumer protection and the continued growth of influencer marketing as a legitimate and trustworthy advertising platform. As the industry further develops, it will be essential for regulators, influencers, and brands to adapt and refine these regulations to guarantee their effectiveness in the ever-changing world of digital marketing, and to guarantee the safeguarding of our youth when they venture to these platforms.
The CAINZ Digest is published by CAINZ, a student society affiliated with the Faculty of Business at the University of Melbourne. Opinions published are not necessarily those of the publishers, printers or editors. CAINZ and the University of Melbourne do not accept any responsibility for the accuracy of information contained in the publication.